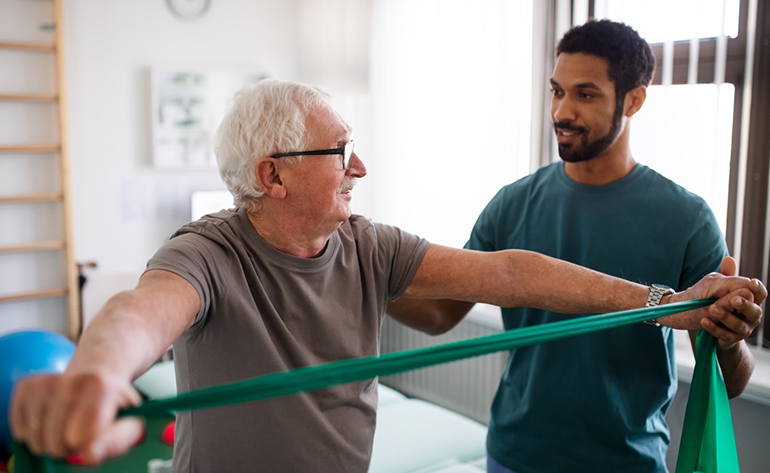
Therapeutic Exercises
Therapeutic exercise involves movement prescribed to correct impairments, restore muscular and skeletal function and/or maintain a state of well-being. Therapeutic exercise is a type of physical activity used to treat or prevent injuries and improve functional outcomes. The scientific evidence demonstrating the beneficial effects of exercise is indisputable, and the benefits of exercise far outweigh the risks in most adults. For most adults, an exercise program including aerobic, resistance, flexibility, and neuromotor exercise training is indispensable to improve and maintain physical fitness and health.
Therapeutic exercise a core skills upon which the profession of physiotherapy is based. How does exercise differ from physical activity?
- Physical activity refers to the contraction of skeletal muscle that produces bodily movement and requires energy.
- Exercise is a physical activity that is planned and is performed with the goal of attaining or maintaining physical fitness. Physical fitness is a set of traits that allows an individual to perform physical activity.
Types of exercises
Therapeutic exercise may include:
- aerobic and endurance conditioning and reconditioning
- agility training;
- body mechanics training;
- breathing exercises;
- coordination exercises;
- developmental activities training;
- movement pattern training;
- neuromotor development activities training;
- neuromuscular education or reeducation;
- perceptual training;
- range of motion exercises and soft tissue stretching;
- relaxation exercises;
- strength, power, and endurance exercises.